
Pulmonary Sequestration
Cardio-thoracic SurgeryPaediatricsPaediatric Surgery
Pulmonary sequestration is a rare congenital lung anomaly, characterized by a portion of lung tissue that does not connect to the normal bronchial tree and receives its blood supply from the systemic circulation (e.g., aorta) rather than the pulmonary arteries. This sequestered lung tissue is non-functioning and prone to infection or abscess formation.
Types of Pulmonary Sequestration
Pulmonary sequestration is a congenital lung anomaly characterized by a portion of lung tissue that does not participate in normal respiration and receives its blood supply from systemic arteries (e.g., the aorta) rather than the pulmonary artery.
Normal Anatomy | 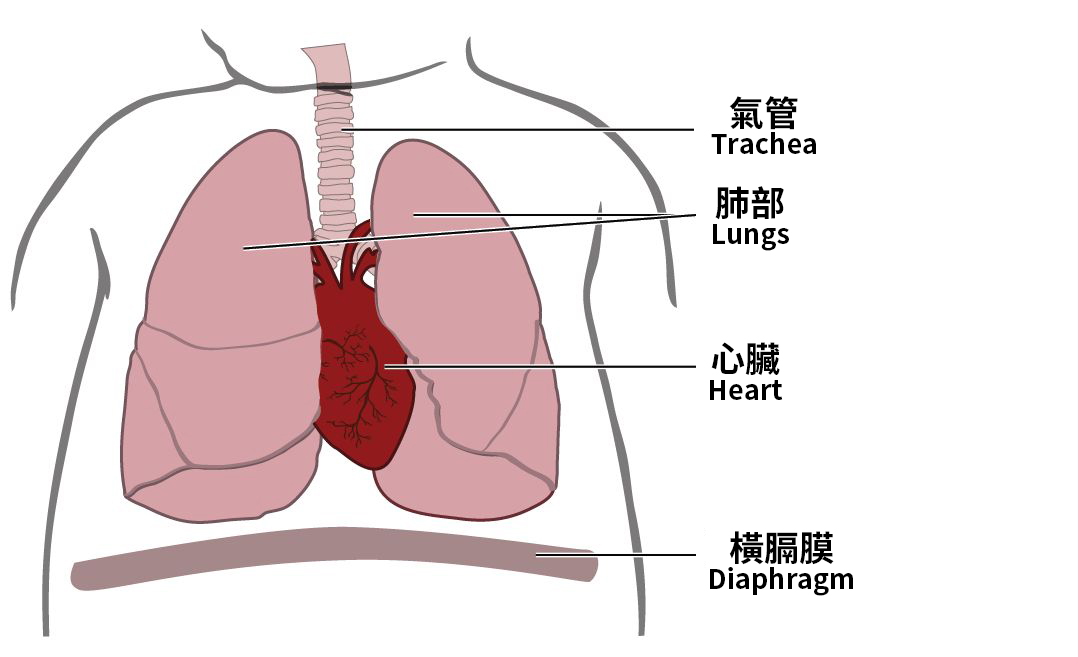 |
Intralobar SequestrationThe sequestered tissue lies within a normal lobe, without a separate pleural covering (more common).
| 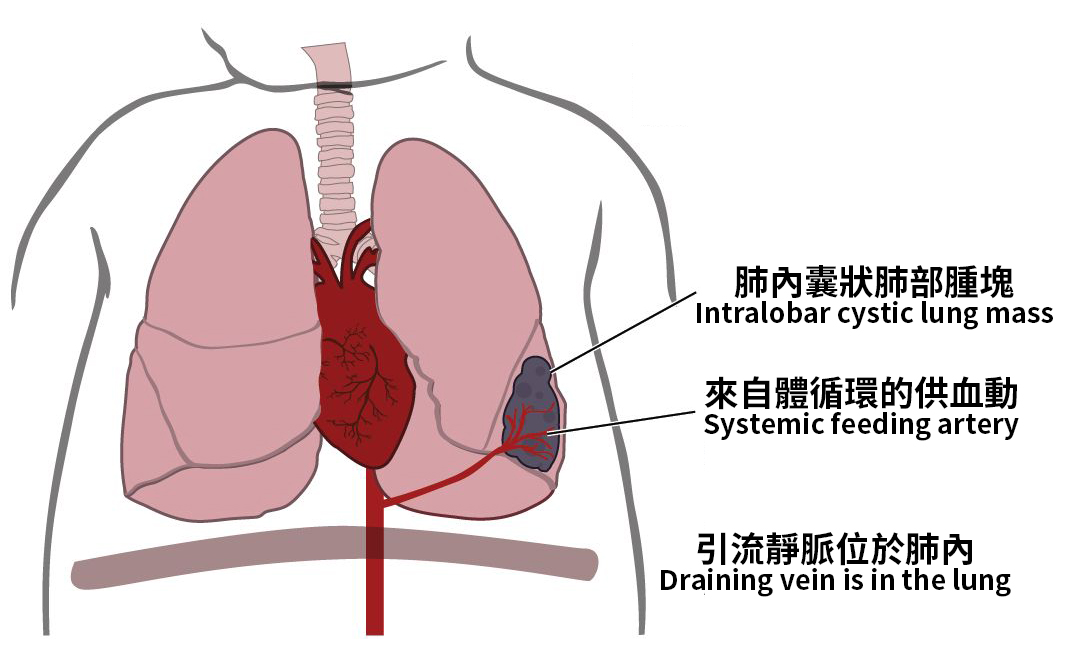 |
Extralobar SequestrationThe sequestered tissue is completely separate from normal lung and has its own pleura.
| 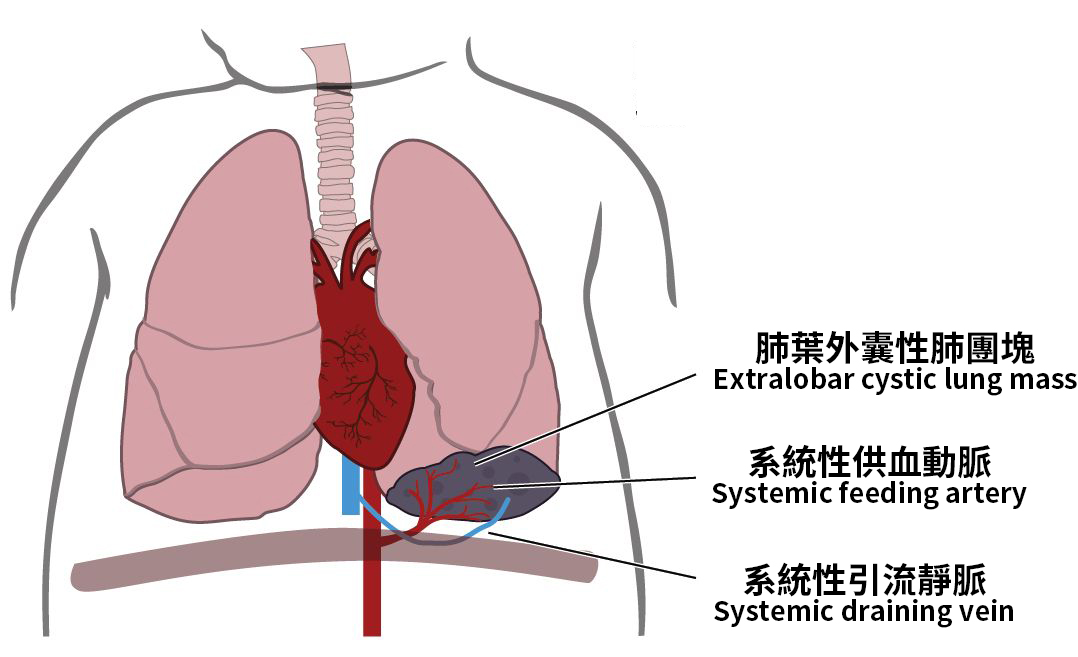 |
Common Symptoms
Symptoms are often related to recurrent lung infections, though some cases may be asymptomatic and discovered incidentally:
- Persistent or recurrent coughing
- Chronic productive cough, sometimes with blood
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
- Fever
- Chest pain (occasional)
- In infants: respiratory distress or poor growth
⚠ Untreated, the abnormal tissue may lead to lung abscesses or bleeding.
Causes & Risk Factors
Pulmonary sequestration is a congenital malformation, present from fetal development. Though the exact cause is unclear, it is believed to be due to abnormal budding of the lung tissue during embryogenesis.
Risk factors include:
- Abnormal thoracic development in the fetus
- May occur with other congenital anomalies (e.g., diaphragmatic hernia)
Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis requires imaging studies to assess anatomy and blood supply:
- Chest X-ray: May show abnormal lung shadows, but cannot identify the vascular supply.
- CT Thorax with Contrast / CT Angiography: Commonly used; clearly shows the abnormal tissue and feeding artery.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): Radiation-free, suitable for children or specific patient groups.
- Prenatal Ultrasound: May be detected during fetal scans.
- Conventional Angiography: Used when planning interventional treatment.
Treatments
Surgery |
|
Interventional Embolization | For patients who are unfit for surgery, embolization of the feeding artery can cause the abnormal tissue to shrink. |
FAQ
Related Doctors

Dr CHU Shun Him Colin
Specialist in Cardio-thoracic Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)

Dr YU Sze Yuen
Specialist in Cardio-thoracic Surgery
HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)
-min.jpg)
Dr MOU Wai Cheung
Specialist in Paediatric Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)

Dr Alan SIHOE Dart Loon
Specialist in Cardio-Thoracic Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)
Related Services
Acute Appendicitis
Anal Fissure
Anal Fistula
Related Articles










Here When You Need Us
HEAL Medical (Central)
A multi-specialty centre providing premium outpatient services for primary and specialist care.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)
Providing comprehensive and high-quality specialist medical services to patients.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Oncology
A boutique oncology centre providing comprehensive day procedure care.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Fertility
Providing world class reproductive medicine services in a friendly, non-judgemental environment.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed


