
Cancer
Clinical OncologyGeneral SurgeryGynaecological OncologyPlastic SurgeryUrologyTraditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
Cancer is the generic name given to a cluster of related diseases. In a normal healthy body, human cells grow and divide as the body needs them. When cells become old or damaged, they die and new cells take their place. However, cancer relates to body cells dividing uncontrollably and spreading to neighbouring tissues. Many cancers form masses of tissues which we call tumour. However, there are certain types of cancer, such as Leukemia that do not form solid tumours.
According to a report jointly published by the Department of Health, Food and Health Bureau and the Hospital Authority there were over 30,000 new cases of cancer registered in 2017. The annual number of cancer cases is projected to increase to over 40,000 cases by 2030.
However due to the advancements across a number of treatment modality the survival rate of patients in also on the increase.
Cancer Staging System
Cancer is typically labelled in stages from I to IV with IV being the most severe. The staging describes the size of the cancer and how far it has spread, if at all. When you are diagnosed with cancer, your doctor will tell you what stage it is.
It’s important to understanding your cancer stage for a number of reasons:
- TREATMENT: It helps your doctor to figure out the best form of treatment based on precedence, if available. An early stage cancer may be treated by surgery, while advanced stage cancer may need chemotherapy.
- OUTLOOK: Your speed of recovery will be largely dependent on how early the cancer is detected. The stage gives you an idea of possible outcomes.
- RESEARCH: Hospitals and healthcare institutions around the world work with cancer databases that keep track treatments used, and how well they have worked.
Researchers as well as your doctor can use this body of knowledge to help you develop your treatment plan.
Most cancer that involve a turmoil are staged in five broad groups. Other kinds of cancer like cancer of the blood and brain cancer have their own staging system.
| Stage O | There is no cancer. Only the potential of abnormal cells of becoming cancerous cells. This is also called Carcinoma in situ. |
| Stage I | Cancer is call and only in one specific area. This is also called early stage cancer. |
| Stage II and III | The tumour is often larger and has grown to neighbouring tissue or lymph node. |
| Stage IV | The cancer has spread to other parts of the body and it is also called advanced or metastatic cancer. |
Cancer Categories
Cancer can spread to almost every organ in the body. The types of cancer are broadly organised into carcinoma, sarcoma, melanoma, lymphoma and leukaemia . Carciomas are the most commonly diagnosed type. They originate in the skin, lungs, breasts, pancreas and other organs and glands. Sarcoma are cancers that are found in bone, muscle, fat blood vessels, cartilage and other soft connective tissues in our bodies. Lymphomas are cancers of the lymphatic system. And melanomas are cancers of the cells that make up the pigment in our skin.
Types of Cancer
Cancer Treatments
Cancer treatment varies based on the type of cancer, stage, and survival rate differences. It is also influenced by factors such as the location, size, and quantity of tumours, so the treatment required for each patient is unique.
Some cancer patients may only require a single treatment method, but for most cancer patients, combining different treatment methods is quite common, such as surgery combined with chemotherapy, surgery combined with radiation therapy, and so on. In addition, cancer treatment can be divided into local treatment and systemic treatment. Local treatment targets the tumour area or specific body parts, while systemic therapy may affect the entire body.

| Surgical Treatment | The purpose of surgery is to remove all identified cancer cells. Most cancer patients require surgery, especially when dealing with tumours in a specific location. While some cancer patients may only need surgery as treatment, in general, surgery is often combined with other therapies. |
| Chemotherapy | Chemotherapy, or "chemo," refers to the use of chemical substances to treat various diseases, gradually evolving into one of the treatment methods specifically for cancer. It involves introducing drugs into the patient's bloodstream to circulate and kill cancer cells. |
| Radiotherapy | Radiotherapy involves using high-energy radiation to irradiate cancer cells inside the patient's body, destroying their chromosomes and preventing them from growing. |
| Brachytherapy | It involves placing radioactive material inside the tumour and continuously irradiating it at close range. There are two methods: sealed radiation sources inserted from behind or unsealed radiation sources for oral or injected treatment. |
| Targeted Therapy | Similar to chemotherapy, targeted therapy kills cancer cells within the patient's body using drugs. However, while chemotherapy targets cells that divide faster, targeted therapy interferes with specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth and survival – the "targets." |
| Immunotherapy | The body's immune system attacks foreign "invaders," such as bacteria, to maintain health. Typically, cancer cells growing suddenly in the body should also be a target of the immune system, but this is not guaranteed. Some cancer cells release signals that can hide them from the immune system or even disable the immune system. Immunotherapy drugs called "immune checkpoint inhibitors" can intercept signals of cancer cell release, making it easier for the immune system to recognize them. |
| Hormone Therapy | Also known as hormone therapy, it interferes with or blocks the body's hormones that some malignant tumours depend on for growth, helping slow down and inhibit the growth of cancer cells. |
| Bone Marrow Transplantation | Bone marrow transplantation, also known as stem cell transplantation, is typically used for patients with cancers such as leukaemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, neuroblastoma, etc. When cancer cells exist in the bone marrow, it is necessary to eliminate all cancer cells first, and then healthy stem cells are transplanted to rebuild normal stem cells and blood cells. |
| Photodynamic Therapy | Photodynamic therapy treats diseases, including cancer, using photosensitizers and light of a specific wavelength. Photosensitizers are injected into the patient's body, and when exposed to sunlight, they produce reactive oxygen species that can destroy abnormal cells or tumour tissues, causing cell death or apoptosis. |
| Proton Therapy | Proton therapy is a new form of radiation therapy that uses proton beams instead of conventional X-rays to treat cancer. This treatment helps precisely target the tumour, reducing damage to surrounding normal tissues. |
| Cryotherapy | A practical method for treating musculoskeletal tumours, cryotherapy involves rapidly freezing and slowly thawing, causing water molecules inside and outside the cells to form ice crystals and aggregate, destroying tumour cells. |
| Ablation Therapy |
|
Before undergoing treatment, a team of oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and radiation therapists work together to devise the most suitable treatment plan for the patient, aiming for optimal therapeutic results while minimizing damage to normal tissues. Factors considered include the type of tumour, its location, size, nearby organs, and the patient's overall health.
Date of Cancer in Hong Kong
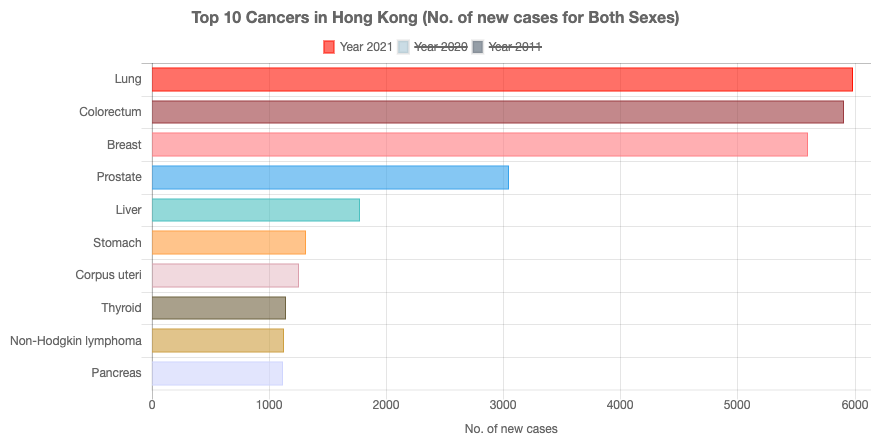
| Incidence in 2021 - Both Sexes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Site | No. | Rel. Freq. | Crude rate* |
| 1 | Lung | 5,978 | 15.5% | 80.6 |
| 2 | Colorectum | 5,899 | 15.3% | 79.6 |
| 3 | Breast | 5,592 | 14.5% | 75.4 |
| 4 | Prostate | 3,038 | 7.9% | 89.8 |
| 5 | Liver | 1,771 | 4.6% | 23.9 |
| 6 | Stomach | 1,306 | 3.4% | 17.6 |
| 7 | Corpus uteri | 1,250 | 3.2% | 31.0 |
| 8 | Thyroid | 1,140 | 3.0% | 15.4 |
| 9 | Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 1,124 | 2.9%. | 15.2 |
| 10 | Pancreas | 1,116 | 2.9% | 15.1 |
| All Sites (Include other sites not listed above) | 38,462 | 100% | 518.8 | |
| Mortality in 2021 - Both Sexes | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Site | No. | Rel. Freq. | Crude rate* |
| 1 | Lung | 4,037 | 26.7% | 54.5 |
| 2 | Colorectum | 2,298 | 15.2% | 31.0 |
| 3 | Liver | 1,447 | 9.6% | 19.5 |
| 4 | Pancreas | 889 | 5.9% | 12.0 |
| 5 | Breast | 795 | 5.3% | 10.7 |
| 6 | Stomach | 631 | 4.2% | 8.5 |
| 7 | Prostate | 518 | 3.4% | 15.3 |
| 8 | Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 388 | 2.6% | 5.2 |
| 9 | Leukaemia | 349 | 2.3% | 4.7 |
| 10 | Oesophagus | 299 | 2.0% | 4.0 |
| All Sites (Include other sites not listed above) | 15,108 | 100.0% | 203.8 | |
*of incidence and mortality are expressed per 100,000 population. Rates for gender-specific sites are per 100,000 male or female population. The figures from 2017 to 2019 have been revised based on the population benchmark from the results of the 2021 Population Census.
HEAL Oncology Centre
We provide a variety of treatment options for different types of cancer, including surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, and traditional Chinese medicine. Our multidisciplinary team of specialists will tailor the best treatment plan for each patient, providing comprehensive and holistic care to ensure you receive the best possible outcomes and support throughout your cancer treatment journey.
HEAL Oncology Centre
16/F, Entertainment Building, 30 Queens Road Central, Central, Hong Kong
Mon - Fri 9:00am - 6:00pm
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

Related Doctors

Dr Oswens LO Siu Hung
Specialist in General Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)
HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)

Dr Henry SZE Chun Kin
Specialist in Clinical Oncology
HEAL Oncology

Dr CHEUNG Chung Yeung
Specialist in General Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)
HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)

Dr Mandy CHU Man Yee
Specialist in Gynaecological Oncology
HEAL Medical (Central)
HEAL Fertility

Dr Johnny LAU Kin Sang
Specialist in Clinical Oncology
HEAL Oncology

Dr Raymond NG Wai Man
Specialist in Plastic Surgery
HEAL Medical (Central)

Dr Anna TAI Yin Ping
Specialist in Clinical Oncology
HEAL Oncology

Dr Jason WONG Ka Wing
Specialist in Urology
HEAL Medical (Central)
HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)

Dr LEUNG To Wai
Specialist in Clinical Oncology
HEAL Oncology

CMP Keith KWAN Ching Ho
Registered Chinese Medicine Practitioner
HEAL Medical (Central)
HEAL Oncology

PhD Wendy WONG
Visiting Consultant of Registered Chinese Medicine Practitioner
HEAL Oncology

Dietitian Sally POON Shi Po
Registered Dietitian (UK) Accredited Practising Dietitian (Australia)
HEAL Medical (Central)
Related Services
Abnormal Menstrual Cycle & Uterine Bleeding
Acute Appendicitis
Acute Cholecystitis
Related Articles














.jpg)









.jpg)






.jpg)




.jpg)



















































.jpg)
Here When You Need Us
HEAL Medical (Central)
A multi-specialty centre providing premium outpatient services for primary and specialist care.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Medical (Tsim Sha Tsui)
Providing comprehensive and high-quality specialist medical services to patients.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Oncology
A boutique oncology centre providing comprehensive day procedure care.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed

HEAL Fertility
Providing world class reproductive medicine services in a friendly, non-judgemental environment.
Sat 9:00am - 1:00pm
Sun & Public Holidays Closed


